Last update images today Decoding The Skies: Weather Maps Unveiled
Decoding the Skies: Weather Maps Unveiled
Introduction
Ever wondered how weather forecasters seemingly predict the future? The secret lies, in part, with synoptic weather maps. These complex charts are more than just pretty pictures; they are powerful tools that unlock the secrets of atmospheric behavior. This week, let's delve into the fascinating world of synoptic charts and explore how they help us forecast weather patterns.
Target Audience: Anyone curious about weather forecasting, students learning about meteorology, outdoor enthusiasts, and those who want to better understand weather reports.
How Can Synoptic Weather Maps Help Us Forecast Weather Patterns?
1. Understanding the Basics: What is a Synoptic Weather Map?
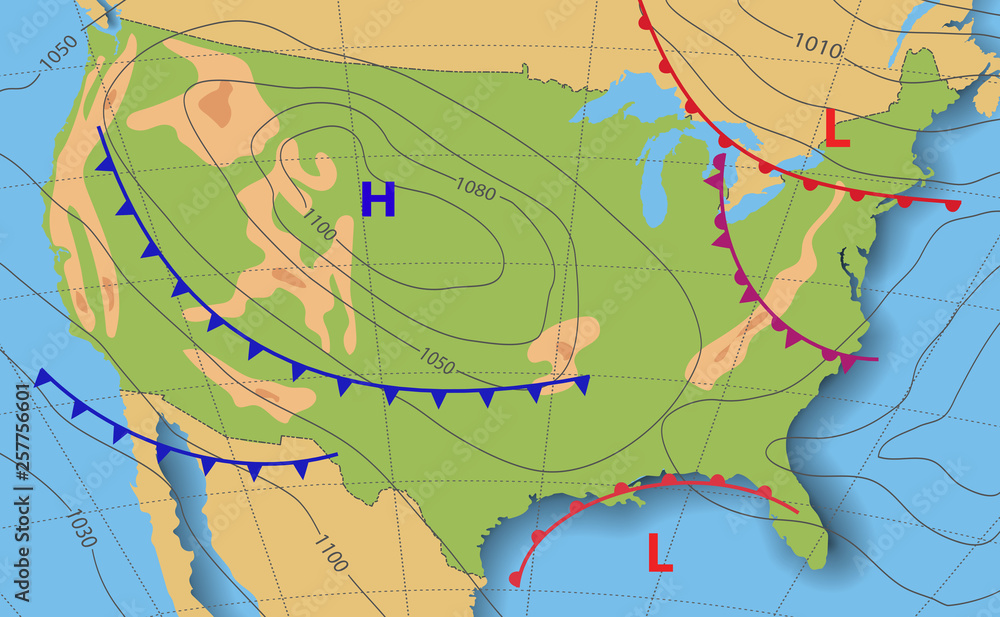
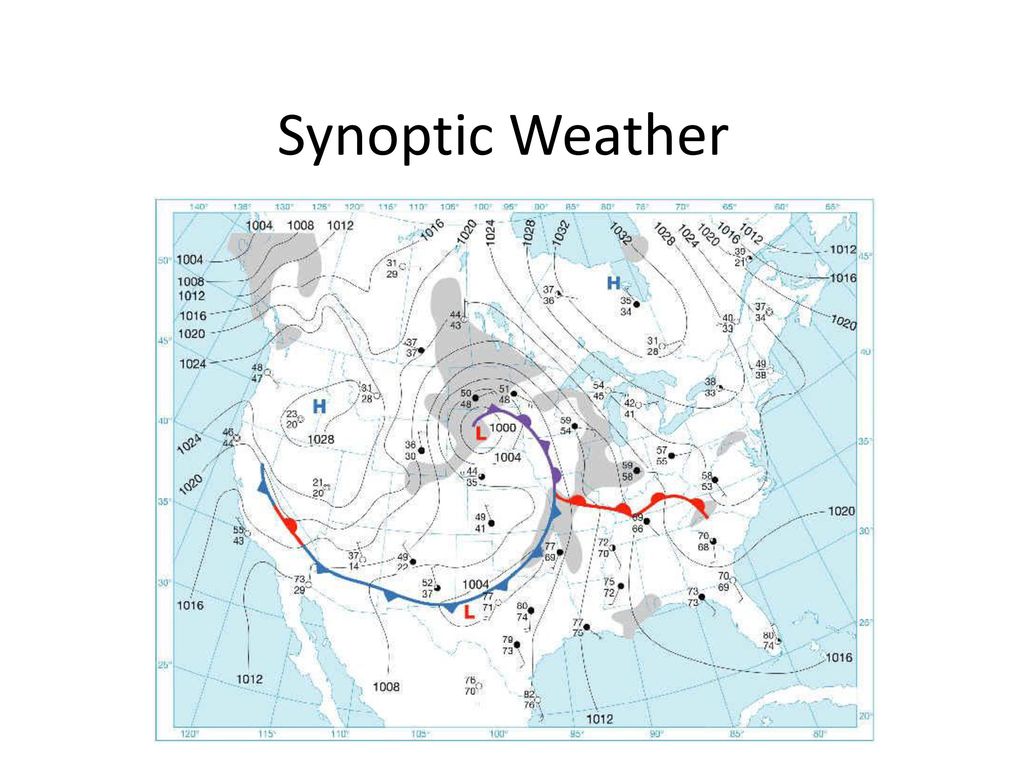
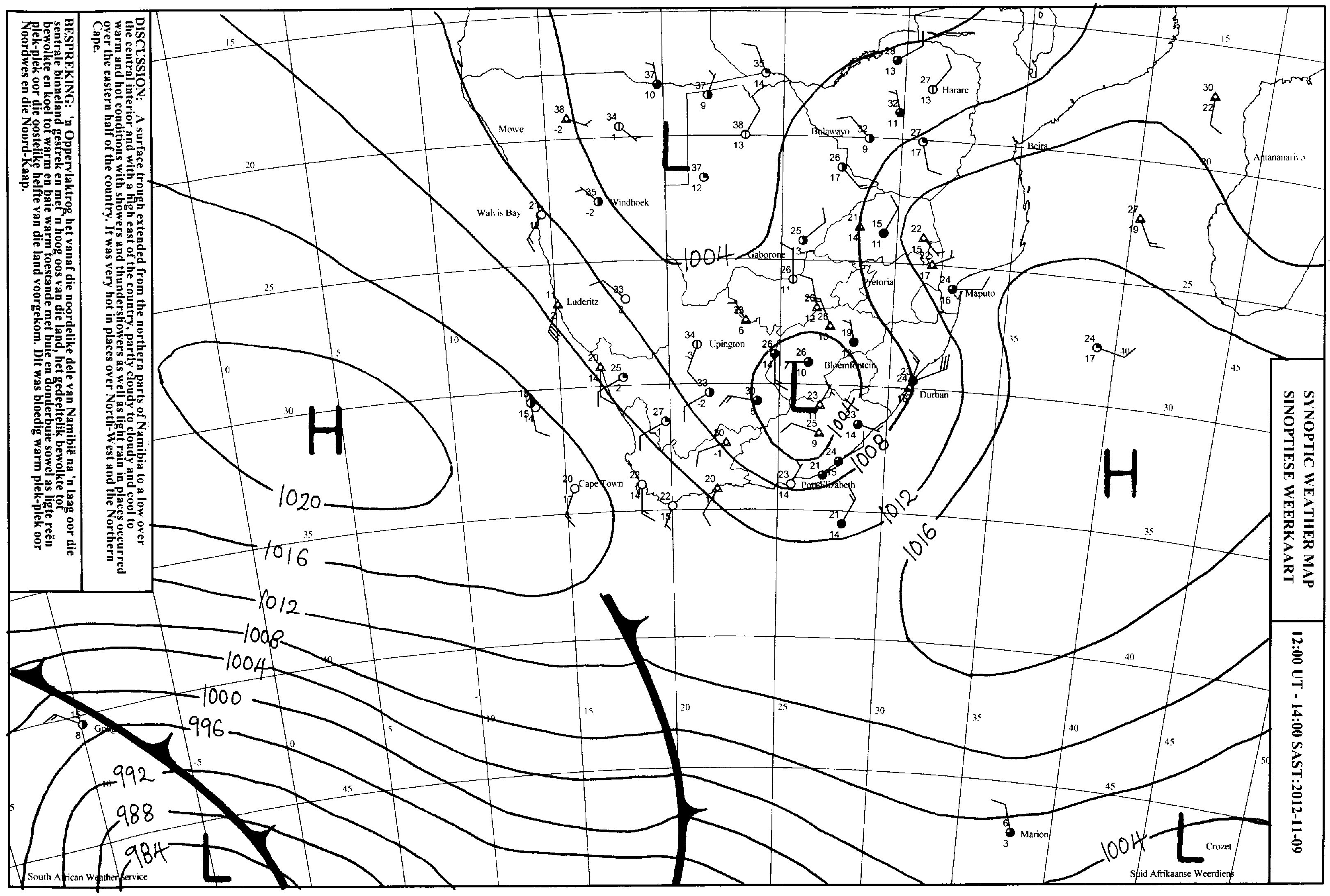
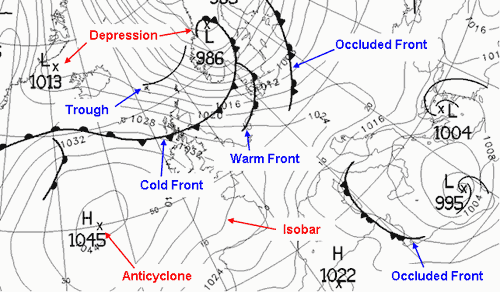
A synoptic weather map, also known as a surface analysis chart, is a snapshot of atmospheric conditions at a specific point in time over a large geographical area. These maps compile data from various sources, including weather stations, buoys, ships, and satellites. The data is then analyzed and depicted using symbols, lines, and colors to represent different weather elements.
ALT Text: Example of a Synoptic Weather Map with fronts, isobars, and weather symbols. Caption: A typical synoptic weather map showing various weather features.
How Can Synoptic Weather Maps Help Us Forecast Weather Patterns? These maps generally include:
- Isobars: Lines connecting points of equal atmospheric pressure. These lines indicate pressure gradients, which are directly related to wind speed and direction. Tightly packed isobars indicate strong winds.
- Fronts: Boundaries between air masses of different temperatures and densities. Common types include cold fronts (leading edge of colder air), warm fronts (leading edge of warmer air), stationary fronts (neither advancing nor retreating), and occluded fronts (where a cold front overtakes a warm front).
- High and Low-Pressure Systems: Indicated by "H" and "L," respectively. High-pressure systems are generally associated with clear skies and stable conditions, while low-pressure systems often bring cloudiness, precipitation, and unsettled weather.
- Wind Direction and Speed: Represented by wind barbs. The direction of the barb indicates the wind direction, and the flags and pennants indicate the wind speed.
- Temperature and Dew Point: Numerical values representing the air temperature and dew point temperature at specific locations.
- Precipitation: Areas of rain, snow, sleet, or hail are often indicated with shading or specific symbols.
- Cloud Cover: Shown using symbols to represent the amount of cloud cover at different locations.
2. Identifying Weather Systems and Patterns
How Can Synoptic Weather Maps Help Us Forecast Weather Patterns? Synoptic maps allow meteorologists to identify and track weather systems, such as cyclones, anticyclones, and fronts. By observing the movement and evolution of these systems, forecasters can predict their future position and intensity.
- Tracking Fronts: Monitoring the movement of cold fronts helps predict when and where colder air will arrive, often accompanied by a period of precipitation and strong winds. Similarly, tracking warm fronts helps predict the arrival of warmer air, usually preceded by cloudiness and light precipitation.
- Analyzing Pressure Systems: Low-pressure systems are associated with rising air, which leads to cloud formation and precipitation. By analyzing the intensity and movement of low-pressure systems, forecasters can predict the likelihood and intensity of rainfall or snowfall. High-pressure systems, on the other hand, are associated with sinking air, which inhibits cloud formation and leads to clear skies.
ALT Text: Depiction of a cold front moving across a region. Caption: A cold front bringing cooler temperatures and precipitation.
3. Predicting Wind Speed and Direction
How Can Synoptic Weather Maps Help Us Forecast Weather Patterns? The spacing of isobars on a synoptic map is directly related to the wind speed. Tightly packed isobars indicate a strong pressure gradient, which results in strong winds. The wind direction can also be determined from the isobars; winds generally blow parallel to the isobars, with a slight deflection towards lower pressure in the Northern Hemisphere due to the Coriolis effect.
- Gale Warnings: By analyzing the isobar patterns, forecasters can identify areas where gale-force winds are likely, issuing warnings to mariners and coastal communities.
- Wind Energy Forecasting: Accurate wind speed and direction predictions are crucial for wind energy production. Synoptic maps provide valuable information for forecasting wind power generation.
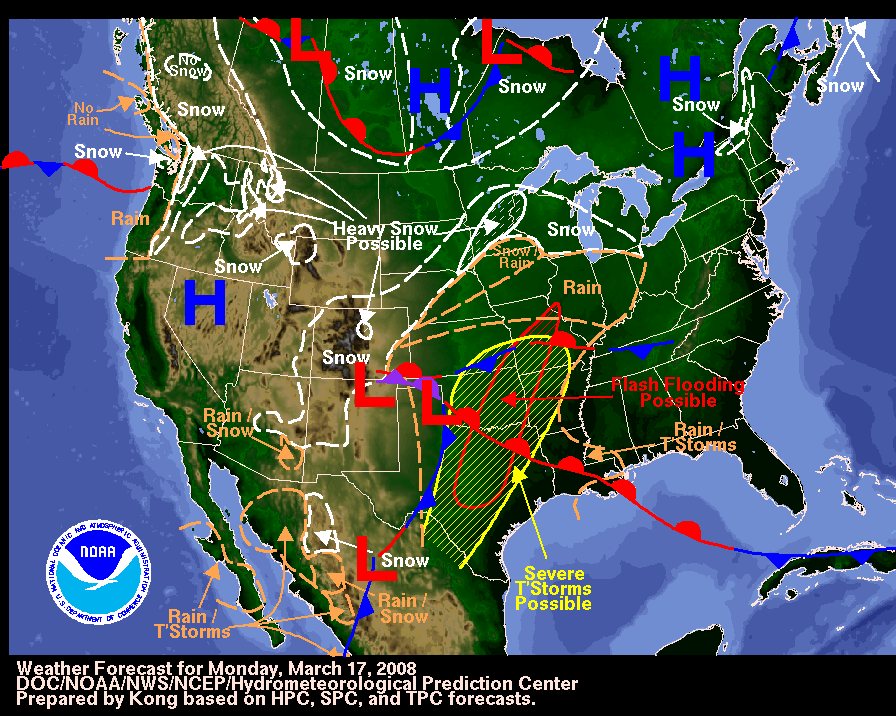
4. Forecasting Precipitation
How Can Synoptic Weather Maps Help Us Forecast Weather Patterns? Synoptic maps help predict the type, intensity, and duration of precipitation. The presence of fronts, low-pressure systems, and areas of convergence (where air masses collide) are all indicators of potential precipitation.
- Frontal Precipitation: When a warm, moist air mass encounters a cold air mass along a front, the warm air is forced to rise, leading to condensation and precipitation. The type of precipitation (rain, snow, sleet, or freezing rain) depends on the temperature profile of the atmosphere.
- Orographic Precipitation: When air is forced to rise over mountains, it cools and condenses, leading to increased precipitation on the windward side of the mountains. Synoptic maps can help identify areas where orographic precipitation is likely.
ALT Text: Illustration of orographic lift causing precipitation on a mountainside. Caption: Orographic lift: Air rising over a mountain creates clouds and precipitation.
5. Identifying Atmospheric Stability
How Can Synoptic Weather Maps Help Us Forecast Weather Patterns? Atmospheric stability refers to the tendency of the atmosphere to either resist or enhance vertical motion. Stable atmospheres tend to suppress cloud formation and precipitation, while unstable atmospheres promote the development of thunderstorms and other severe weather. Synoptic maps provide clues about atmospheric stability, such as temperature and dew point profiles, as well as the presence of inversions (where temperature increases with height).
- Thunderstorm Potential: By analyzing atmospheric stability parameters, forecasters can assess the likelihood of thunderstorm development. Unstable atmospheres with high levels of moisture are favorable for thunderstorms.
- Fog Formation: Stable atmospheres with light winds and clear skies are conducive to fog formation. Synoptic maps can help identify areas where fog is likely to form.
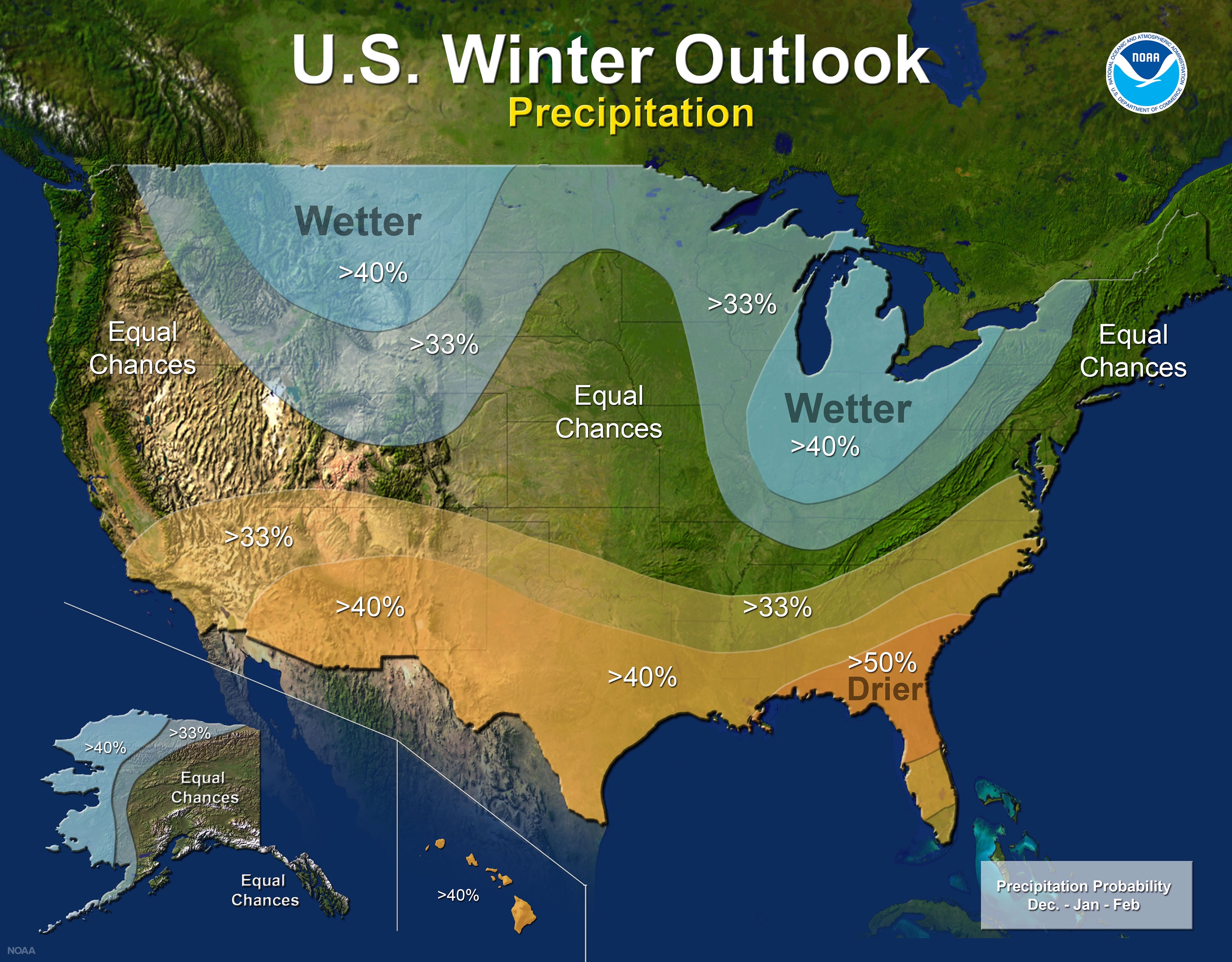
6. Beyond the Surface: Upper-Air Charts
While surface synoptic maps provide a snapshot of conditions at ground level, upper-air charts depict conditions at various altitudes in the atmosphere. These charts are essential for understanding the large-scale atmospheric circulation and for predicting the development and movement of weather systems.
- Jet Stream Analysis: Upper-air charts show the location and strength of the jet stream, a fast-flowing current of air in the upper atmosphere. The jet stream plays a crucial role in steering weather systems and influencing surface weather patterns.
- Vertical Wind Shear: Upper-air charts can also be used to assess vertical wind shear, which is the change in wind speed and direction with height. Vertical wind shear is an important factor in the development of severe thunderstorms, including tornadoes.
Conclusion
Synoptic weather maps are indispensable tools for weather forecasting. By providing a comprehensive view of atmospheric conditions, these maps enable meteorologists to identify weather systems, predict their movement and intensity, and forecast various weather elements such as temperature, wind, and precipitation. Understanding how to interpret synoptic maps can enhance our appreciation of the weather and improve our ability to prepare for its impacts.
Keywords: synoptic weather map, weather forecasting, meteorology, fronts, isobars, high pressure, low pressure, wind, precipitation, atmospheric stability, weather patterns, jet stream.
Summary Question and Answer:
Q: How do synoptic weather maps help us forecast weather patterns?
A: Synoptic weather maps display real-time atmospheric conditions, allowing forecasters to identify and track weather systems like fronts and pressure centers, predict wind speed and direction, forecast precipitation, and assess atmospheric stability, ultimately leading to more accurate weather predictions.
























Synoptic Charts And Weather Weather Systems Revision BBC Bitesize SmallSynoptic Weather Maps Station Data And Analysis At A 500 HPa And B Synoptic Weather Maps Station Data And Analysis At A 500hPa And B 850hPa On May 25 Fillable Online How Can Synoptic Weather Maps Help Us Forecast Fax Large What Can A Synoptic Map Tell Us About The Weather Windy App IMG 2537.PNGWhat Is A Synoptic Weather Map Station Models Image 7 June 10 2025 Weather Forecast Katrin L Krause 56601c7168156fc603919c23a8f53fe7d24a2579fc4b S1000 830x662
Weather Patterns And Maps Ppt Download Weather Forecasting Synoptic Map Forecast Weather Map Meteorological Weather Map Infographic Template Forecast Weather Map Meteorological Infographic Template Climate Generic System Synoptic Prediction Pressure Direction 248004439 What Is A Synoptic Weather Map Station Models Image 2 This Is How Every Weather Forecast Map Should Look Like How To Read A Weather Map Weather Maps Depicting The Synoptic Weather Conditions During The 21 Weather Maps Depicting The Synoptic Weather Conditions During The 21 Aug 2017 Eclipse Q640 Synoptic Weather Ppt Download Synoptic Weather General Meteorology And Their Application Towards Forecasting Ppt The Word Synoptic Means View Together Or View At A Common Point
What Are Synoptic Weather Map WorldMap US Cb3bb73b0a7d31af620abd543a9187c9 What Can A Synoptic Map Tell Us About The Weather Windy App IMG 2539.PNGWill It Snow In Alabama This Year 2025 Logan G Strange 5641 Weather Forecast Meteorological Weather Map Of The United State Of 1000 F 257756601 H09eOVKIJ99cm8TY6wsXlOunRl0MtbU1 Synoptic Weather Map Interpreting Grade 12 Geography YouTube Maxresdefault Isobar Weather Map Synoptic 20121109 Typical Surface Maps Of Synoptic Weather Patterns Associated With Five Typical Surface Maps Of Synoptic Weather Patterns Associated With Five Storm Types What Can A Synoptic Map Tell Us About The Weather Windy App IMG 2538.PNG
Synoptic Charts Archives MetLink Royal Meteorological Society Fig 3 April 2025 Weather Predictions Map Nora Leen US Forecast Map Features Of A Synoptic Chart Keski 11 Sample Pacific Wx Map Interp Solved 9 Discussion How Can Synoptic Weather Maps Help Us Chegg Com ImageForecasting The Weather Ppt Download Example Of A Synoptic Weather Map. Us Synoptic Weather Map Corene Charlotte Synoptic Map Soln Weather Forecasting Observations Sharing Data Synoptic Charts Original 8914152 4
Synoptic Weather Maps For January 15th Top Left Panel And January Synoptic Weather Maps For January 15th Top Left Panel And January 25th Top Right Q640 Forecast Weather Map Of America Topography Map With Geography Forecast Weather Map America Topography Geography Landforms Elevation Template Synoptic Movement Fronts Cyclone 249118414 Topic IV Meteorology Ppt Download B. Synoptic Weather Maps Show Weather Conditions On A National Or Global Basis.

